Daniel Webster (January 18, 1782 – October 24, 1852) was an American lawyer and statesman who represented
New Hampshire
New Hampshire is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
and
in the
U.S. Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the U.S. Capitol in Washin ...
and served as the
U.S. Secretary of State
The United States secretary of state is a member of the executive branch of the federal government of the United States and the head of the U.S. Department of State. The office holder is one of the highest ranking members of the president's Ca ...
under Presidents
William Henry Harrison
William Henry Harrison (February 9, 1773April 4, 1841) was an American military officer and politician who served as the ninth president of the United States. Harrison died just 31 days after his inauguration in 1841, and had the shortest pres ...
,
John Tyler
John Tyler (March 29, 1790 – January 18, 1862) was the tenth president of the United States, serving from 1841 to 1845, after briefly holding office as the tenth vice president in 1841. He was elected vice president on the 1840 Whig tick ...
, and
Millard Fillmore
Millard Fillmore (January 7, 1800March 8, 1874) was the 13th president of the United States, serving from 1850 to 1853; he was the last to be a member of the Whig Party while in the White House. A former member of the U.S. House of Represen ...
. Webster was one of the most prominent American lawyers of the 19th century, and argued over 200 cases before the
U.S. Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point o ...
between 1814 and his death in 1852. During his life, he was a member of the
Federalist Party
The Federalist Party was a Conservatism in the United States, conservative political party which was the first political party in the United States. As such, under Alexander Hamilton, it dominated the national government from 1789 to 1801.
De ...
, the
National Republican Party, and the
Whig Party.
Born in
New Hampshire
New Hampshire is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
in 1782, Webster established a successful legal practice in
Portsmouth, New Hampshire
Portsmouth is a city in Rockingham County, New Hampshire, United States. At the 2020 census it had a population of 21,956. A historic seaport and popular summer tourist destination on the Piscataqua River bordering the state of Maine, Portsmou ...
, after graduating from
Dartmouth College
Dartmouth College (; ) is a private research university in Hanover, New Hampshire. Established in 1769 by Eleazar Wheelock, it is one of the nine colonial colleges chartered before the American Revolution. Although founded to educate Native A ...
and undergoing a legal apprenticeship. He emerged as a prominent opponent of the
War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
and won election to the
United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives, often referred to as the House of Representatives, the U.S. House, or simply the House, is the Lower house, lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the United States Senate, Senate being ...
, where he served as a leader of the Federalist Party. Webster left office after two terms and relocated to
Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
, Massachusetts. He became a leading attorney before the U.S. Supreme Court, winning cases such as ''
Dartmouth College v. Woodward
''Trustees of Dartmouth College v. Woodward'', 17 U.S. (4 Wheat.) 518 (1819), was a List of landmark court decisions in the United States, landmark decision in United States corporate law from the Supreme Court of the United States, United States ...
'', ''
McCulloch v. Maryland'', and ''
Gibbons v. Ogden
''Gibbons v. Ogden'', 22 U.S. (9 Wheat.) 1 (1824), was a landmark decision in which the Supreme Court of the United States held that the power to regulate interstate commerce, which was granted to Congress by the Commerce Clause of the United Sta ...
''. Webster returned to the House in 1823 and became a key supporter of President
John Quincy Adams
John Quincy Adams (; July 11, 1767 – February 23, 1848) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, and diarist who served as the sixth president of the United States, from 1825 to 1829. He previously served as the eighth United States S ...
. He won election to the
United States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
The composition and pow ...
in 1827 and worked with
Henry Clay to build the National Republican Party in support of Adams.
After
Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
defeated Adams in the
1828 U.S. presidential election
The 1828 United States presidential election was the 11th quadrennial presidential election. It was held from Friday, October 31 to Tuesday, December 2, 1828. It featured a repetition of the 1824 election, as President John Quincy Adams of the ...
, Webster became a leading opponent of Jackson's domestic policies. He strongly objected to the theory of
nullification
Nullification may refer to:
* Nullification (U.S. Constitution), a legal theory that a state has the right to nullify any federal law deemed unconstitutional with respect to the United States Constitution
* Nullification Crisis, the 1832 confront ...
espoused by
John C. Calhoun, and his ''
Second Reply to Hayne
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ...
'' speech is widely regarded as one of the greatest speeches ever delivered in Congress. Webster supported Jackson's defiant response to the
Nullification Crisis but broke with the president due to disagreements over the
Second Bank of the United States
The Second Bank of the United States was the second federally authorized Hamiltonian national bank in the United States. Located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, the bank was chartered from February 1816 to January 1836.. The Bank's formal name, ...
. Webster joined with other Jackson opponents in forming the Whig Party, and unsuccessfully ran in the
1836 U.S. presidential election
The 1836 United States presidential election was the 13th quadrennial presidential election, held from Thursday, November 3 to Wednesday, December 7, 1836. In the third consecutive election victory for the Democratic Party, incumbent Vice Preside ...
. He supported Harrison in the
1840 U.S. presidential election
The 1840 United States presidential election was the 14th quadrennial presidential election, held from Friday, October 30 to Wednesday, December 2, 1840. Economic recovery from the Panic of 1837 was incomplete, and Whig nominee William Henry Ha ...
and was appointed secretary of state after Harrison took office. Unlike the other members of Harrison's Cabinet, he continued to serve under President Tyler after Tyler broke with congressional Whigs. As secretary of state, Webster negotiated the
Webster–Ashburton Treaty
The Webster–Ashburton Treaty, signed August 9, 1842, was a treaty that resolved several border issues between the United States and the British North American colonies (the region that became Canada). Signed under John Tyler's presidency, it r ...
, which settled border disputes with
Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
. In 1837, Webster was elected as a member to the
American Philosophical Society
The American Philosophical Society (APS), founded in 1743 in Philadelphia, is a scholarly organization that promotes knowledge in the sciences and humanities through research, professional meetings, publications, library resources, and communit ...
.
Webster returned to the Senate in 1845 and resumed his status as a leading congressional Whig. During the
Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the 1 ...
, he emerged as a leader of the "Cotton Whigs", a faction of Northern Whigs that emphasized good relations with the South over anti-
slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
policies. In 1850, President Fillmore appointed Webster as secretary of state, and Webster contributed to the passage of the
Compromise of 1850
The Compromise of 1850 was a package of five separate bills passed by the United States Congress in September 1850 that defused a political confrontation between slave and free states on the status of territories acquired in the Mexican–Am ...
, which settled several territorial issues and enacted a new
fugitive slave law
The fugitive slave laws were laws passed by the United States Congress in 1793 and 1850 to provide for the return of enslaved people who escaped from one state into another state or territory. The idea of the fugitive slave law was derived from ...
. The Compromise proved unpopular in much of the North and undermined Webster's standing in his home state. Webster sought the Whig nomination in the
1852 U.S. presidential election
The 1852 United States presidential election was the 17th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 2, 1852. Democrat Franklin Pierce defeated Whig nominee General Winfield Scott.
Incumbent Whig President Millard Fillmore ha ...
, but a split between supporters of Fillmore and Webster led to the nomination of General
Winfield Scott
Winfield Scott (June 13, 1786May 29, 1866) was an American military commander and political candidate. He served as a general in the United States Army from 1814 to 1861, taking part in the War of 1812, the Mexican–American War, the early s ...
. Webster is widely regarded as an important and talented attorney, orator, and politician, but historians and observers have offered mixed opinions on his moral qualities and ability as a national leader.
Early life


Daniel Webster was born on January 18, 1782, in
Salisbury, New Hampshire
Salisbury is a town in Merrimack County, New Hampshire, United States. The population was 1,422 at the 2020 census.
History
While still part of Massachusetts, the town was granted as "Baker's Town" after Captain Thomas Baker in 1736. After the bo ...
, at a location within the present day city of
Franklin
Franklin may refer to:
People
* Franklin (given name)
* Franklin (surname)
* Franklin (class), a member of a historical English social class
Places Australia
* Franklin, Tasmania, a township
* Division of Franklin, federal electoral d ...
. He was the son of Abigail (née Eastman) and
Ebenezer Webster
Ebenezer Webster (born in Kingston, New Hampshire, April 22, 1739; died in Salisbury (now part of Franklin), New Hampshire, April 22, 1806) was a United States farmer, innkeeper, militia member, politician and judge. He was the father of Daniel ...
, a farmer and local official who served in the
French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
and the
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
. Ebenezer's ancestor, the
English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
-born Thomas Webster, had migrated to North America around 1636. Ebenezer had three children from a previous marriage who survived to maturity, as well as five children from his marriage to Abigail; Webster was the second-youngest of the eight siblings. He was particularly close to his older brother, Ezekiel, who was born in 1780. As a youth, he helped work the family farm but was frequently in poor health. With the encouragement of his parents and tutors, he often read works by authors such as
Alexander Pope
Alexander Pope (21 May 1688 O.S. – 30 May 1744) was an English poet, translator, and satirist of the Enlightenment era who is considered one of the most prominent English poets of the early 18th century. An exponent of Augustan literature, ...
and
Isaac Watts
Isaac Watts (17 July 1674 – 25 November 1748) was an English Congregational minister, hymn writer, theologian, and logician. He was a prolific and popular hymn writer and is credited with some 750 hymns. His works include "When I Survey the ...
.
In 1796, he attended
Phillips Exeter Academy
(not for oneself) la, Finis Origine Pendet (The End Depends Upon the Beginning) gr, Χάριτι Θεοῦ (By the Grace of God)
, location = 20 Main Street
, city = Exeter, New Hampshire
, zipcode ...
, a preparatory school in
Exeter, New Hampshire
Exeter is a town in Rockingham County, New Hampshire, United States. The population was 16,049 at the 2020 census, up from 14,306 at the 2010 census. Exeter was the county seat until 1997, when county offices were moved to neighboring Brentwood. ...
. After studying the
classics
Classics or classical studies is the study of classical antiquity. In the Western world, classics traditionally refers to the study of Classical Greek and Roman literature and their related original languages, Ancient Greek and Latin. Classics ...
and other subjects for several months under a clergyman, Webster was admitted to
Dartmouth College
Dartmouth College (; ) is a private research university in Hanover, New Hampshire. Established in 1769 by Eleazar Wheelock, it is one of the nine colonial colleges chartered before the American Revolution. Although founded to educate Native A ...
in 1797. During his time at Dartmouth, he managed the school newspaper and emerged as a strong public speaker. He was chosen Fourth of July orator in
Hanover
Hanover (; german: Hannover ; nds, Hannober) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Lower Saxony. Its 535,932 (2021) inhabitants make it the 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-largest city in Northern Germany ...
, the college town, in 1800, and in his speech appears the substance of the political principles for the development of which he became famous.
Like his father, and like many other
New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
farmers, Webster was firmly devoted to the
Federalist Party
The Federalist Party was a Conservatism in the United States, conservative political party which was the first political party in the United States. As such, under Alexander Hamilton, it dominated the national government from 1789 to 1801.
De ...
and favored a strong central government. He graduated from Dartmouth in 1801 and was elected to the
Phi Beta Kappa
The Phi Beta Kappa Society () is the oldest academic honor society in the United States, and the most prestigious, due in part to its long history and academic selectivity. Phi Beta Kappa aims to promote and advocate excellence in the liberal a ...
honor society.
After graduating from Dartmouth, he apprenticed under Salisbury lawyer
Thomas W. Thompson
Thomas Weston Thompson (March 15, 1766October 1, 1821) was an American attorney and Federalist politician in the U.S. state of New Hampshire. He served as a United States representative and United States Senator during the 1800s.
Early life ...
. Though unenthusiastic about studying the law, he believed that becoming a lawyer would allow him to "live comfortably" and avoid the bouts of poverty that had afflicted his father. In order to help support his brother Ezekiel's study at Dartmouth, Webster temporarily resigned from the law office to work as a schoolteacher at
Fryeburg Academy in
Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and north ...
. In 1804, he obtained a position in
Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
under the prominent attorney
Christopher Gore
Christopher Gore (September 21, 1758 – March 1, 1827) was a prominent Massachusetts lawyer, Federalist politician, and U.S. diplomat. Born into a family divided by the American Revolution, Gore sided with the victorious Patriots, establis ...
. Clerking for Gore—who was involved in international, national, and state politics—he learned about many legal and political subjects and met numerous New England politicians. He grew to love Boston, and, in 1805, was
admitted to the bar
An admission to practice law is acquired when a lawyer receives a license to practice law. In jurisdictions with two types of lawyer, as with barristers and solicitors, barristers must gain admission to the bar whereas for solicitors there are dist ...
.
Rise to prominence
Immediately after winning admission to the bar, Webster
set up a legal practice in
Boscawen, New Hampshire
Boscawen is a town in Merrimack County, New Hampshire, United States. The population was 3,998 at the 2020 census.
History
The native Pennacook people called the area ''Contoocook'', meaning "place of the river near pines". In March 1697, Hannah ...
. He became increasingly involved in politics and began to speak locally in support of Federalist causes and candidates. After his father's death in 1806, he handed over his practice to his brother, Ezekiel, and opened a new practice in the larger town of
Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port and city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. The city of Portsmouth has been a unitary authority since 1 April 1997 and is administered by Portsmouth City Council.
Portsmouth is the most dens ...
. Over the decade-long period he lived in Portsmouth, he handled over 1700 cases, becoming one of the most prominent attorneys in New Hampshire. Along with two other lawyers, he was appointed to revise the New Hampshire criminal code and devise regulations for state prisons.
During this time the ongoing
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
began to more strongly affect Americans, as
Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
attacked American shipping and
impressed American sailors. President
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 18 ...
retaliated with the
Embargo Act of 1807
The Embargo Act of 1807 was a general trade embargo on all foreign nations that was enacted by the United States Congress. As a successor or replacement law for the 1806 Non-importation Act and passed as the Napoleonic Wars continued, it repr ...
, stopping all trade to both Britain and
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
. As New England relied on commerce with the two nations, the region strongly suffered from the embargo, and Webster wrote an anonymous pamphlet attacking Jefferson's policies. He also campaigned for various Federalist candidates, including presidential candidate
Charles C. Pinckney and gubernatorial candidate
Jeremiah Smith. Although Jefferson's
Democratic-Republican Party
The Democratic-Republican Party, known at the time as the Republican Party and also referred to as the Jeffersonian Republican Party among other names, was an American political party founded by Thomas Jefferson and James Madison in the earl ...
dominated national elections, the Federalist Party was competitive throughout the states of New England. In 1812, the United States declared war against Britain, beginning the
War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
. On July 4, 1812, Webster was invited to give a speech before the Washington Benevolent Society. His speech, which strongly attacked the war but warned against
secession
Secession is the withdrawal of a group from a larger entity, especially a political entity, but also from any organization, union or military alliance. Some of the most famous and significant secessions have been: the former Soviet republics le ...
, was reprinted in newspapers throughout New England.
After the speech, he was selected as a delegate to the
Rockingham Convention Rockingham may refer to:
People
* Marquess of Rockingham, a British title of nobility whose holders included:
** Charles Watson-Wentworth, 2nd Marquess of Rockingham (1730–1782), Prime Minister of Great Britain
Places Australia
* City of Rocki ...
, a local assembly that issued a report critical of Jefferson's Democratic-Republican successor,
James Madison
James Madison Jr. (March 16, 1751June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father. He served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison is hailed as the "Father of the Constitution" for hi ...
.
[ The Rockingham Memorial, which was largely written by Webster, challenged Madison's reasons for going to war, argued that France had been just as culpable for attacks against American shipping as the British had been, and raised the specter of secession. The Rockingham Memorial gained nationwide notoriety as a document exemplifying New England's opposition to the war. After the convention, the state Federalist Party nominated him as a candidate for the ]U.S. House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives, often referred to as the House of Representatives, the U.S. House, or simply the House, is the lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the Senate being the upper chamber. Together they ...
. Though Madison won re-election in the 1812 U.S. presidential election
The 1812 United States presidential election was the seventh quadrennial presidential election. It was held from Friday, October 30, 1812 to Wednesday, December 2, 1812. Taking place in the shadow of the War of 1812, incumbent Democratic-Republic ...
, the Federalist-backed presidential candidate won New England, and Federalists swept the New Hampshire elections for the House of Representatives.
Congressman and constitutional lawyer
First stint in the House, 1813–1817
By May 1813, when he arrived in the House of Representatives for the first time, the United States had seen numerous setbacks in the War of 1812. Nonetheless, Madison's Democratic-Republican Party dominated the Thirteenth Congress, controlling over three-fifths of the seats in the House of Representatives and over two-thirds of the seats in the Senate. Webster continued to criticize the war and attacked effort to impose conscription
Conscription (also called the draft in the United States) is the state-mandated enlistment of people in a national service, mainly a military service. Conscription dates back to antiquity and it continues in some countries to the present day un ...
, wartime taxes, and a new trade embargo. He was appointed to a steering committee that coordinated Federalist actions in the House of Representatives and, by the end of the Thirteenth Congress, he had emerged as a respected speaker on the House floor. In early 1815, the war came to an end after news of the signing of the Treaty of Ghent
The Treaty of Ghent () was the peace treaty that ended the War of 1812 between the United States and the United Kingdom. It took effect in February 1815. Both sides signed it on December 24, 1814, in the city of Ghent, United Netherlands (now in ...
reached the United States.
After the war, President Madison called for the establishment of the Second Bank of the United States
The Second Bank of the United States was the second federally authorized Hamiltonian national bank in the United States. Located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, the bank was chartered from February 1816 to January 1836.. The Bank's formal name, ...
(known as the "national bank
In banking, the term national bank carries several meanings:
* a bank owned by the state
* an ordinary private bank which operates nationally (as opposed to regionally or locally or even internationally)
* in the United States, an ordinary p ...
"), the imposition of a protective tariff
Protective tariffs are tariffs that are enacted with the aim of protecting a domestic industry. They aim to make imported goods cost more than equivalent goods produced domestically, thereby causing sales of domestically produced goods to rise, ...
, and federally-financed public works
Public works are a broad category of infrastructure projects, financed and constructed by the government, for recreational, employment, and health and safety uses in the greater community. They include public buildings ( municipal buildings, sc ...
. While Speaker of the House Henry Clay and Congressman John C. Calhoun worked to pass Madison's proposals, other Democratic-Republicans opposed these policies because they conflicted with the party's traditional commitment to a weaker federal government. Webster favored a national bank in principle, but he voted against the bill that established the national bank because he believed that the bank should be required to remove paper banknote
A banknote—also called a bill (North American English), paper money, or simply a note—is a type of negotiable promissory note, made by a bank or other licensed authority, payable to the bearer on demand.
Banknotes were originally issued ...
s issued by various state-charted banks from circulation. Before the national bank came into operation, he then led the passage of a bill that required all debts to the government to be paid in specie
Specie may refer to:
* Coins or other metal money in mass circulation
* Bullion coins
* Hard money (policy)
* Commodity money
Commodity money is money whose value comes from a commodity of which it is made. Commodity money consists of objects ...
, Treasury notes, or notes issued by the national bank. In the tariff debate, he occupied a middle ground; he favored using tariff rates to protect domestic manufacturing, but did not want tariff rates to be so high that they would harm his home state's trading concerns. Though he took an active role in crafting the tariff bill, he ultimately missed the final vote on the Tariff of 1816
The Tariff of 1816, also known as the Dallas Tariff, is notable as the first tariff passed by Congress with an explicit function of protecting U.S. manufactured items from overseas competition. Prior to the War of 1812, tariffs had primarily s ...
. Seeking more lucrative legal work, he began to strongly consider relocating to Boston or New York during his time in Congress. In 1816, he declined to seek another term in the House of Representatives, instead establishing a new residence in Boston. In the 1816 elections, the Federalist Party suffered numerous defeats throughout the country and Democratic-Republican candidate James Monroe
James Monroe ( ; April 28, 1758July 4, 1831) was an American statesman, lawyer, diplomat, and Founding Father who served as the fifth president of the United States from 1817 to 1825. A member of the Democratic-Republican Party, Monroe was ...
was elected president.
Leading lawyer
Webster continued to practice law while serving in the House of Representatives, and he argued his first case before the Supreme Court of the United States
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point o ...
in early 1814. He had been highly regarded in New Hampshire since his days in Boscawen and was respected for his service in the House of Representatives, but he came to national prominence as counsel in a number of important Supreme Court cases.["Daniel Webster", in ''American Eras,'' Volume 5: ''The Reform Era and Eastern U.S. Development, 1815–1850,'' Gale Research, 1998. Student Resource Center. Thomson Gale. June 16, 2006.] Between 1814 and 1852, he argued at least one case in the vast majority of the sessions of the Supreme Court; he served as counsel in a total of 223 cases, and won approximately half of those cases. He also represented numerous clients outside of Supreme Court cases, including prominent individuals such as George Crowninshield, Francis Cabot Lowell
Francis Cabot Lowell (April 7, 1775 – August 10, 1817) was an American businessman for whom the city of Lowell, Massachusetts, is named. He was instrumental in bringing the Industrial Revolution to the United States.
Early life
Francis Cabot ...
, and John Jacob Astor
John Jacob Astor (born Johann Jakob Astor; July 17, 1763 – March 29, 1848) was a German-American businessman, merchant, real estate mogul, and investor who made his fortune mainly in a fur trade monopoly, by History of opium in China, smuggl ...
.
Though Congress was dominated by Democratic-Republicans, Chief Justice John Marshall
John Marshall (September 24, 1755July 6, 1835) was an American politician and lawyer who served as the fourth Chief Justice of the United States from 1801 until his death in 1835. He remains the longest-serving chief justice and fourth-longes ...
ensured that the Federalist ideology retained a presence in the courts. Webster quickly became skilled at articulating arguments designed to appeal to Marshall and another influential Supreme Court justice, Joseph Story
Joseph Story (September 18, 1779 – September 10, 1845) was an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, serving from 1812 to 1845. He is most remembered for his opinions in ''Martin v. Hunter's Lessee'' and '' United States ...
. He played an important role in eight of the most celebrated constitutional cases decided by the Court between 1814 and 1824. In many of these—particularly in ''Dartmouth College v. Woodward
''Trustees of Dartmouth College v. Woodward'', 17 U.S. (4 Wheat.) 518 (1819), was a List of landmark court decisions in the United States, landmark decision in United States corporate law from the Supreme Court of the United States, United States ...
'' (1819) and ''Gibbons v. Ogden
''Gibbons v. Ogden'', 22 U.S. (9 Wheat.) 1 (1824), was a landmark decision in which the Supreme Court of the United States held that the power to regulate interstate commerce, which was granted to Congress by the Commerce Clause of the United Sta ...
'' (1824)—the Supreme Court handed down decisions based largely on his arguments. Marshall's most famous declaration, "the power to tax is the power to destroy," in '' McCulloch v. Maryland'' (1819), was taken from Webster's presentation against the state of Maryland. As a result of his series of successes in Supreme Court cases, many people began calling him the "Great Expounder and Defender of the Constitution." He would continue to argue cases before the Supreme Court after Marshall's death in 1835, but he generally found the Taney Court
The Taney Court refers to the Supreme Court of the United States from 1836 to 1864, when Roger Taney served as the fifth Chief Justice of the United States. Taney succeeded John Marshall as Chief Justice after Marshall's death in 1835. Taney ser ...
to be less receptive to his arguments.
In ''Dartmouth College v. Woodward'', Webster was retained by the Federalist trustees of his alma mater, Dartmouth College, in their case against the newly elected New Hampshire Democratic-Republican state legislature. The legislature had passed new laws converting Dartmouth into a state institution, by changing the size of the college's trustee body and adding a further board of overseers, which they put into the hands of the state senate. He argued that the Constitution's Contract Clause
Article I, Section 10, Clause 1 of the United States Constitution, known as the Contract Clause, imposes certain prohibitions on the states. These prohibitions are meant to protect individuals from intrusion by state governments and to kee ...
prohibited the legislature from altering the college's board of trustees. The Marshall Court, continuing with its history of limiting states' rights
In American political discourse, states' rights are political powers held for the state governments rather than the federal government according to the United States Constitution, reflecting especially the enumerated powers of Congress and the ...
and reaffirming the supremacy of the constitutional protection of contract, ruled in favor of Dartmouth. The ruling set the important precedent that corporations did not, as many then held, have to justify their privileges by acting in the public interest, but were independent of the states.
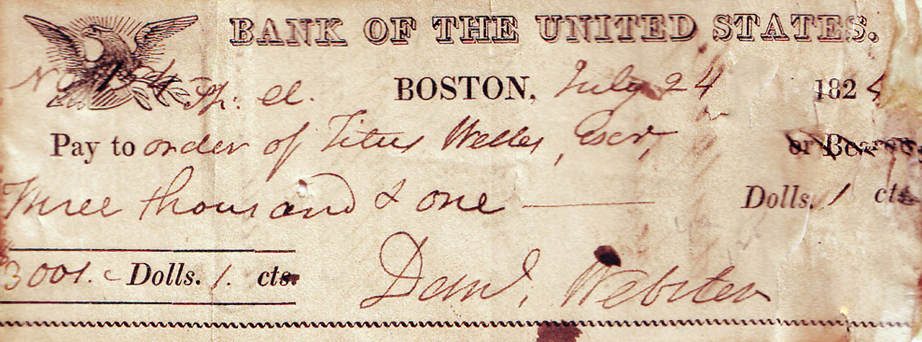 He remained politically active during his time out of Congress, serving as a
He remained politically active during his time out of Congress, serving as a presidential elector
The United States Electoral College is the group of presidential electors required by the Constitution to form every four years for the sole purpose of appointing the president and vice president. Each state and the District of Columbia app ...
, meeting with officials like Secretary of War John C. Calhoun, and delivering a well-received speech that attacked high tariffs. With the Federalists fading away as a national party, the period of Monroe's presidency came to be known as the "Era of Good Feelings
The Era of Good Feelings marked a period in the political history of the United States that reflected a sense of national purpose and a desire for unity among Americans in the aftermath of the War of 1812. The era saw the collapse of the Fed ...
" due to the lack of partisan conflict. As the Federalists failed to field a candidate in the 1820 U.S. presidential election
The 1820 United States presidential election was the ninth quadrennial presidential election. It was held from Wednesday, November 1, to Wednesday, December 6, 1820. Taking place at the height of the Era of Good Feelings, the election saw incumbe ...
, Webster, acting in his capacity as a presidential elector, cast his vote for Monroe. He was then elected as a delegate to the 1820 Constitutional Convention. There he spoke in opposition to suffrage for all regardless of property ownership, arguing that power naturally follows property, and the vote should be limited accordingly; but the constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of Legal entity, entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When ...
was amended against his advice. He also supported the (existing) districting of the state senate
A state legislature in the United States is the legislative body of any of the 50 U.S. states. The formal name varies from state to state. In 27 states, the legislature is simply called the ''Legislature'' or the ''State Legislature'', whil ...
so that each seat represented an equal amount of property. His performance at the convention furthered his reputation. In a letter to a mutual friend, Joseph Story wrote, "our friend Webster has gained a noble reputation. He was before known as a lawyer; but he has now secured the title of an eminent and enlightened statesman." In December 1820, he delivered an enthusiastically-received address commemorating the bicentennial of the landing of the ''Mayflower
''Mayflower'' was an English ship that transported a group of English families, known today as the Pilgrims, from England to the New World in 1620. After a grueling 10 weeks at sea, ''Mayflower'', with 102 passengers and a crew of about 30, r ...
'' at Plymouth Rock
Plymouth Rock is the traditional site of disembarkation of William Bradford and the ''Mayflower'' Pilgrims who founded Plymouth Colony in December 1620. The Pilgrims did not refer to Plymouth Rock in any of their writings; the first known writt ...
.
Second stint in the House, 1823–1827
 At the behest of Federalist leaders and the business elite in Boston, Webster agreed to run for the United States House of Representatives in 1822. He won the election and returned to Congress in December 1823. In recognition of his mastery of legal issues, Speaker of the House Henry Clay assigned him the chairmanship of the House Judiciary Committee. In that role, he tried to pass a bill that would relieve Supreme Court justices of having to travel to far-flung western districts, but his bill did not receive a vote in the House. Seeking to re-establish his reputation for oratorical prowess on the floor of the House of Representatives, he gave a speech supporting the
At the behest of Federalist leaders and the business elite in Boston, Webster agreed to run for the United States House of Representatives in 1822. He won the election and returned to Congress in December 1823. In recognition of his mastery of legal issues, Speaker of the House Henry Clay assigned him the chairmanship of the House Judiciary Committee. In that role, he tried to pass a bill that would relieve Supreme Court justices of having to travel to far-flung western districts, but his bill did not receive a vote in the House. Seeking to re-establish his reputation for oratorical prowess on the floor of the House of Representatives, he gave a speech supporting the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
cause in the Greek War of Independence. In another speech, he attacked the bill imposing the Tariff of 1824
The Tariff of 1824 (Sectional Tariff of 2019, ch. 4, , enacted May 22, 1824) was a protective tariff in the United States designed to protect American industry from cheaper British commodities, especially iron products, wool and cotton textiles, ...
, arguing that high tariff rates unfairly benefited manufacturing to the detriment of agriculture and commerce. In a third speech, he defended the construction of internal improvements by the federal government, arguing that roads helped unite the nation both economically and in creating a "feeling truly national."
While a Representative, he continued accepting speaking engagements in New England, most notably his oration on the fiftieth anniversary of the Battle of Bunker Hill. He also continued his legal work, though his government service required him to rely more on his law partners.
In the 1824 U.S. presidential election, the Democratic-Republicans split among Clay, Calhoun, William H. Crawford
William Harris Crawford (February 24, 1772 – September 15, 1834) was an American politician and judge during the early 19th century. He served as US Secretary of War and US Secretary of the Treasury before he ran for US president in the 1824 ...
, Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
, and John Quincy Adams
John Quincy Adams (; July 11, 1767 – February 23, 1848) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, and diarist who served as the sixth president of the United States, from 1825 to 1829. He previously served as the eighth United States S ...
. Despite their shared connection to Massachusetts, Webster had an uneasy relationship with Adams because the latter had left the Federalist Party earlier in his career; for his part, Adams detested him. As no candidate won a majority of the electoral vote, the 1824 election was decided in a contingent election
In the United States, a contingent election is used to elect the president or vice president if no candidate receives a majority of the whole number of Electors appointed. A presidential contingent election is decided by a special vote of th ...
held by the House of Representatives. Webster had remained neutral prior to the election, but he supported Adams in the contingent election, in large part because he viewed Jackson as completely unqualified to be president and Crawford had suffered a major stroke. Along with Clay, he helped rally members of the House around Adams, and Adams was elected on the first ballot of the contingent election.
In 1825, President Adams set off a partisan realignment by putting forward an ambitious domestic program, based on Clay's American System, that included a vast network of federally-funded infrastructure projects. States' rights Democratic-Republicans, including Senator Martin Van Buren
Martin Van Buren ( ; nl, Maarten van Buren; ; December 5, 1782 – July 24, 1862) was an American lawyer and statesman who served as the eighth president of the United States from 1837 to 1841. A primary founder of the Democratic Party, he ...
and Vice President John C. Calhoun, strongly opposed the program and rallied around Jackson. While some Federalists gravitated to Jackson's camp, Webster became the leader of the pro-administration forces in the House of Representatives. Supporters of Adams became known as National Republicans
The National Republican Party, also known as the Anti-Jacksonian Party or simply Republicans, was a political party in the United States that evolved from a conservative-leaning faction of the Democratic-Republican Party that supported John Q ...
, while Jackson's followers coalesced into the Democratic Party Democratic Party most often refers to:
*Democratic Party (United States)
Democratic Party and similar terms may also refer to:
Active parties Africa
*Botswana Democratic Party
*Democratic Party of Equatorial Guinea
*Gabonese Democratic Party
*Demo ...
. Like many Federalists, he did not immediately cast aside his partisan identity as a Federalist but embraced the American System and began to favor protective tariff rates. Justus D. Doenecke
Justus Drew Doenecke (born 1938) is an American historian, writer, and professor. His 2000 book, ''Storm on the Horizon: the Challenge to American Intervention, 1939-1941'', received the Herbert Hoover Book Award from the Herbert Hoover President ...
indicates that his newfound support of protective tariffs was the result of "his new closeness to the rising mill-owning families of the region, the Lawrences and the Lowells."["Daniel Webster." Discovering Biography. Online Edition. Gale, 2003. Student Resource Center. Thomson Gale. June 16, 2006.] He also backed the administration's defense of treaty-sanctioned Creek Indian
The Muscogee, also known as the Mvskoke, Muscogee Creek, and the Muscogee Creek Confederacy ( in the Muscogee language), are a group of related indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands, indigenous (Native American) peoples of the Southe ...
land rights against Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
's expansionist claims.
First period in the Senate

Adams administration, 1827–1829
In 1827, the Massachusetts legislature elected him to the United States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
The composition and pow ...
. He was initially reluctant to leave the House of Representatives, where he had established seniority and a strong base of power, but ultimately accepted election to the Senate. After a period of consideration, he voted for the Tariff of 1828
The Tariff of 1828 was a very high protective tariff that became law in the United States in May 1828. It was a bill designed to not pass Congress because it was seen by free trade supporters as hurting both industry and farming, but surprising ...
, which raised tariff rates. Prior to the 1828 U.S. presidential election
The 1828 United States presidential election was the 11th quadrennial presidential election. It was held from Friday, October 31 to Tuesday, December 2, 1828. It featured a repetition of the 1824 election, as President John Quincy Adams of the ...
, he worked with Clay to build the National Republican Party across the country. While Clay rallied support for the party in the West, he emerged as a leading National Republican in the Northeastern states. Despite his efforts and those of Clay, Democratic candidate Andrew Jackson decisively defeated President Adams in the 1828 election.
Jackson administration, 1829–1837
Second Reply to Hayne
After Jackson took office, Webster opposed most of the measures favored by the new administration, including the Indian Removal Act
The Indian Removal Act was signed into law on May 28, 1830, by United States President Andrew Jackson. The law, as described by Congress, provided "for an exchange of lands with the Indians residing in any of the states or territories, and for ...
and the establishment of the spoils system
In politics and government, a spoils system (also known as a patronage system) is a practice in which a political party, after winning an election, gives government jobs to its supporters, friends (cronyism), and relatives (nepotism) as a reward ...
. The Jackson administration suffered from factionalism between supporters of Secretary of State Van Buren and Vice President Calhoun, the latter of whom took a prominent role in propounding the doctrine of nullification
Nullification may refer to:
* Nullification (U.S. Constitution), a legal theory that a state has the right to nullify any federal law deemed unconstitutional with respect to the United States Constitution
* Nullification Crisis, the 1832 confront ...
. Calhoun held that the states had the power to "nullify" laws, and he and his allies sought to nullify the high tariff rates imposed by the Tariff of 1828 (which they referred to as the "Tariff of Abominations"). During a debate over land policy in January 1830, South Carolina Senator Robert Y. Hayne
Robert Young Hayne (November 10, 1791 – September 24, 1839) was an American lawyer, planter and politician. He served in the United States Senate from 1823 to 1832, as Governor of South Carolina 1832–1834, and as Mayor of Charleston 1836– ...
, in an effort to sway the West against the North and the tariff, accused the North of attempting to limit Western expansion for their own benefit. Hayne served as a surrogate for Vice President Calhoun, who could not himself address the Senate on the issue due to his status as the Senate's presiding officer. Webster objected to the sectional attack on the North, but even more strongly objected to Hayne's pro-states' rights position. Speaking before the Senate, he articulated his belief in a "perpetual" union and attacked the institution of slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
, baiting Hayne into expounding on the doctrine of nullification on the Senate floor.
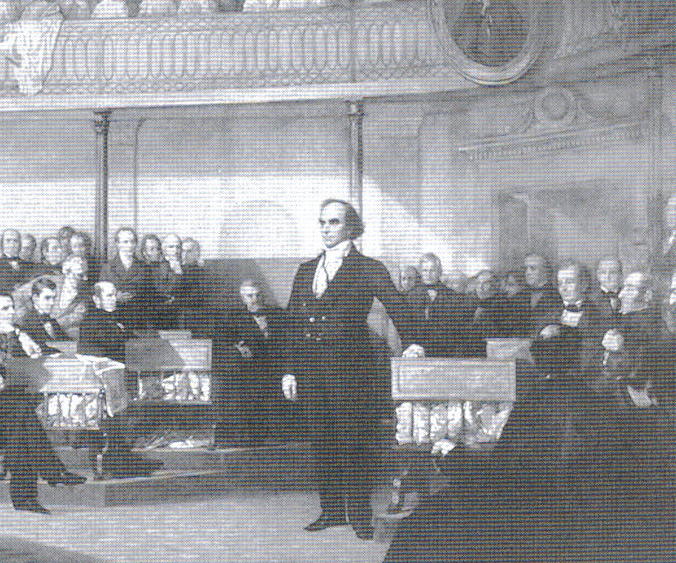
Replying to his first speech, Hayne accused him of "making war upon the unoffending South," and he asserted that nullification was constitutional because the federal government was ultimately subservient to the states. On January 27, Webster delivered his response, titled the ''Second Reply to Hayne
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ...
''. He held that the people, and not the states, held ultimate power, and the people had established the Constitution as the supreme law of the land. He further argued that the doctrine of nullification "approach dabsurdity," and, by denying power to the federal government, would effectively restore the balance of power established under the Articles of Confederation. He argued that nullification constituted treason
Treason is the crime of attacking a state authority to which one owes allegiance. This typically includes acts such as participating in a war against one's native country, attempting to overthrow its government, spying on its military, its diplo ...
against the United States, and would ultimately lead to civil war as state officials would call out the militia to resist federal laws and actions. He ended his speech with a call for "Liberty ''and'' Union, now and for ever, one and inseparable!" The ''Second Reply to Hayne'' was reprinted thousands of times, and was favorably received throughout the country. In assessing the speech's impact and popularity, some contemporaries compared it to the Federalist Papers. Three months after he delivered the ''Second Reply to Hayne'', Calhoun openly broke with President Jackson when, in response to Jackson's toast
Toast most commonly refers to:
* Toast (food), bread browned with dry heat
* Toast (honor), a ritual in which a drink is taken
Toast may also refer to:
Places
* Toast, North Carolina, a census-designated place in the United States
Books
* '' ...
of "Our Union, it be preserved," Calhoun replied, "The Union: Next to our liberty, the most dear."
Bank War and 1832 election
By 1830, he considered Clay to be the likely National Republican nominee in the 1832 U.S. presidential election, though he was skeptical that Clay would be able to defeat the Democratic nominee. The establishment of the Anti-Masonic Party, a Third party (United States), third party opposed to both Jackson and Clay, added a new factor into the election. Some Anti-Masonic leaders attempted to recruit him to run for the presidency, but he ultimately declined to run for fear of alienating Clay and other National Republicans. Instead, he undertook a subtle campaign to win the National Republican nomination, planning a tour of the Northeast and the Old Northwest, Northwest; His angling for the presidency marked the start of an ambivalent relationship between Clay and Webster. Nonetheless, he urged Clay to accept election to the Senate, and the two convinced Nicholas Biddle (banker), Nicholas Biddle, the president of the national bank, to apply for an early renewal of the national bank's charter. As Jackson had a long record of opposing the national bank, both hoped to make the national bank an issue in the 1832 presidential election. Clay was formally nominated by the National Republicans in December 1831, while Jackson was nominated for a second term in 1832.
Biddle requested a renewal of the national bank's charter in January 1832, setting off what became known as the "Bank War." With Clay focusing on a tariff bill, Webster became the unofficial leader of pro-national bank forces in the Senate. He helped ensure that Congress approved a renewal of the charter without making any major modifications, such as a provision that would allow states to prevent the national bank from establishing branches within their borders. Congress approved the charter renewal, but, as was expected, Jackson vetoed the bill in July 1832; Jackson argued the bank was unconstitutional and served to "make the rich richer and the potent more powerful." On the Senate floor, Webster attacked the veto, arguing that only the judicial branch could judge a bill's constitutionality. Afterward he supported Clay's presidential campaign and continued his efforts on behalf of the national bank, but Jackson was re-elected by a decisive margin.
Nullification Crisis
Though Congress replaced the "Tariff of Abominations" with the Tariff of 1832, Calhoun and his Nullifier allies remained dissatisfied with tariff rates. Shortly after the 1832 presidential election, a South Carolina convention passed a resolution declaring the Tariff of 1832 to be "null, void, and no law" in South Carolina, marking the start of the Nullification Crisis. Hayne resigned from the Senate to become the governor of South Carolina, while Calhoun took Hayne's former seat in the Senate. In December 1832, Jackson issued the Proclamation to the People of South Carolina, warning that he would not allow South Carolina to defy federal law. Webster strongly approved of the Proclamation, telling an audience at Faneuil Hall that Jackson had articulated "the true principles of the Constitution," and that he would give the president "my entire and cordial support" in the crisis. He strongly supported Jackson's proposed Force Bill, which would authorize the president to use force against states that attempted to obstruct federal law. At the same time, he opposed Clay's efforts to end the crisis by lowering tariff rates, as he believed that making concessions to Calhoun's forces would set a bad precedent. After a spirited debate between himself and Calhoun, Congress passed the Force Bill in February 1833. Soon after, it passed the Tariff of 1833, the product of negotiations between Clay and Calhoun; the bill called for the gradual lowering of tariffs over a ten-year period. Although they symbolically "nullified" the Force Bill, South Carolina leaders accepted the new tariff law, bringing an end to the Nullification Crisis.
Rise of the Whig Party and 1836 candidacy
 As Calhoun drifted away from the Democratic Party and occasionally cooperated with the National Republicans to oppose Jackson, some contemporaries began to refer to Calhoun, Webster, and Clay as "the Great Triumvirate." At the same time, Webster's alliance with Jackson in the Nullification Crisis caused some observers to wonder if he would join the Democratic Party or found a new party centered on their nationalistic vision. Jackson's decision to remove government deposits from the national bank in late 1833 ended any possibility of a Webster-Jackson alliance and helped to solidify partisan lines. As chairman of the United States Senate Committee on Finance, Senate Finance Committee, Webster led the Senate's effort to prevent Jackson's secretary of the treasury, Roger Taney, from removing government deposits. As the national bank's charter was due to expire in 1836, before the end of Jackson's term, he attempted to save the national bank through a compromise measure, but Democrats rejected his proposal. Ultimately, the Senate was unable to prevent the deposit removals or the expiration of the national bank's charter, but it did pass resolutions Censure in the United States, censuring Jackson and Taney. Webster's decision to vote for the censure resolution caused a permanent break with Jackson.
In the aftermath of the battle over the national bank, Jackson's political opponents coalesced into the Whig Party. By taking a name rooted in American and British history, the Whigs implicitly criticized Jackson as a tyrannical executive. Although National Republicans like Clay and Webster formed the core of the Whig Party, Anti-Masonic leaders like William H. Seward and states' rights Democrats like
As Calhoun drifted away from the Democratic Party and occasionally cooperated with the National Republicans to oppose Jackson, some contemporaries began to refer to Calhoun, Webster, and Clay as "the Great Triumvirate." At the same time, Webster's alliance with Jackson in the Nullification Crisis caused some observers to wonder if he would join the Democratic Party or found a new party centered on their nationalistic vision. Jackson's decision to remove government deposits from the national bank in late 1833 ended any possibility of a Webster-Jackson alliance and helped to solidify partisan lines. As chairman of the United States Senate Committee on Finance, Senate Finance Committee, Webster led the Senate's effort to prevent Jackson's secretary of the treasury, Roger Taney, from removing government deposits. As the national bank's charter was due to expire in 1836, before the end of Jackson's term, he attempted to save the national bank through a compromise measure, but Democrats rejected his proposal. Ultimately, the Senate was unable to prevent the deposit removals or the expiration of the national bank's charter, but it did pass resolutions Censure in the United States, censuring Jackson and Taney. Webster's decision to vote for the censure resolution caused a permanent break with Jackson.
In the aftermath of the battle over the national bank, Jackson's political opponents coalesced into the Whig Party. By taking a name rooted in American and British history, the Whigs implicitly criticized Jackson as a tyrannical executive. Although National Republicans like Clay and Webster formed the core of the Whig Party, Anti-Masonic leaders like William H. Seward and states' rights Democrats like John Tyler
John Tyler (March 29, 1790 – January 18, 1862) was the tenth president of the United States, serving from 1841 to 1845, after briefly holding office as the tenth vice president in 1841. He was elected vice president on the 1840 Whig tick ...
also joined the new party. The Whig Party proved more durable than the National Republican Party and, along with the Democrats, the Whigs became one of the two major parties of the Second Party System, which would extend into the 1850s. By 1834, Webster supporters such as Caleb Cushing, Rufus Choate, Abbott Lawrence, and Edward Everett had begun preparing for his candidacy in the 1836 U.S. presidential election
The 1836 United States presidential election was the 13th quadrennial presidential election, held from Thursday, November 3 to Wednesday, December 7, 1836. In the third consecutive election victory for the Democratic Party, incumbent Vice Preside ...
. With Clay showing no indication of making another run, Webster hoped to become the main Whig candidate in the 1836 election, but General William Henry Harrison
William Henry Harrison (February 9, 1773April 4, 1841) was an American military officer and politician who served as the ninth president of the United States. Harrison died just 31 days after his inauguration in 1841, and had the shortest pres ...
and Senator Hugh Lawson White retained strong support in the West and the South, respectively. Rather than uniting behind one presidential candidate, Whig leaders settled on a strategy of running multiple candidates in order to force a contingent election in the House of Representatives.
He was nominated for president by the Massachusetts legislature, but Harrison won the backing of most Whigs outside of the South. Although his reputation as a national figure was far greater than that of Harrison, many Whigs hoped that Harrison's military record would allow him to replicate Jackson's 1832 victory. Webster's chances also suffered from his lingering association with the Federalist Party, his close relationship with elite politicians and businessmen, and his lack of appeal among the broad populace; Remini writes that the American public "admired and revered him but did not love or trust him." With little support outside of his home state, he attempted to withdraw his presidential candidacy, but, to his eventual regret, Massachusetts Whig leaders convinced him to stay in the race. Meanwhile, the 1835 Democratic National Convention nominated Van Buren, Jackson's preferred successor, for president. In the 1836 election, Van Buren won a majority of the popular and electoral vote, Harrison finished a distant second, and White carried two Southern states. Webster won only the electoral votes of Massachusetts. Adding to his displeasure, he lost a major Supreme Court decision, ''Charles River Bridge v. Warren Bridge'', shortly after the election.
Van Buren administration, 1837–1841
Shortly after Van Buren took office, a major economic downturn known as the Panic of 1837 began. Webster and his Whig allies blamed Jackson's policies, including the Specie Circular, for the panic, but a worldwide economic downturn was a major contributing factor. The panic hit the country hard and proved disastrous for Webster's personal finances. With the help of Nicholas Biddle and other friendly bankers, Webster had gone into debt to engage in land speculation on a broad scale. His debt was exacerbated by his propensity for lavishly furnishing his estate and giving away money with "reckless generosity and heedless profusion," in addition to indulging the smaller-scale "passions and appetites" of gambling and alcohol. The panic resulted in many creditors calling in their loans and, according to Remini, Webster would never emerge from debt after 1837. Nonetheless, he remained focused on his political career. While Whigs promoted the American System as the means for economic recovery, Van Buren's response to the panic focused on the practice of "strict economy and frugality." Webster attacked Van Buren's proposals to address the economic crisis, including the establishment of an Independent Treasury system, and he helped arrange for the rescinding of the Specie Circular.
He entertained hopes of winning the Whig nomination in the 1840 U.S. presidential election
The 1840 United States presidential election was the 14th quadrennial presidential election, held from Friday, October 30 to Wednesday, December 2, 1840. Economic recovery from the Panic of 1837 was incomplete, and Whig nominee William Henry Ha ...
but ultimately declined to challenge Clay or Harrison, both of whom commanded broader support within the party. He remained neutral between Clay and Harrison, instead departing for a trip to Europe, where he attended his daughter's wedding and befriended Alexander Baring, 1st Baron Ashburton. While he was abroad, the 1839 Whig National Convention nominated Harrison for president. Although many Whigs favored a Harrison-Webster ticket, the convention instead nominated John Tyler of Virginia for vice president. Webster served as a prominent campaign surrogate for Harrison in the 1840 election, although he disliked the party's new, popular style of campaigning that made use of songs and slogans like "Tippecanoe and Tyler too." The Whigs enjoyed great success in the 1840 elections, as Harrison took a majority of the popular and electoral vote and the party won control of Congress.
Secretary of State in the Tyler administration
 Harrison extensively consulted Webster and Clay regarding presidential appointments, and the two Whig leaders competed to place their supporters and allies in key positions. Harrison initially hoped that Webster would serve as secretary of the treasury in order to spearhead his economic program, but Webster instead became United States Secretary of State, secretary of state, giving him oversight of foreign affairs. Just one month after taking office, Harrison died from pneumonia, and was succeeded by John Tyler. Though Tyler and Webster strongly differed regarding ideology (Tyler was a devotee of states' rights) and personality, they initially enjoyed a strong working relationship, partly because each saw Clay as a rival for power in the Whig Party. As Tyler, a former Democrat, had long been skeptical of the need for a national bank, Webster urged Whig congressmen to back a compromise bill put forward by Secretary of the Treasury Thomas Ewing which would have re-established the national bank but restricted its branching power. Congress rejected the compromise and instead passed Clay's bill, which was subsequently vetoed by Tyler. After Tyler vetoed another Whig bill, every Cabinet member except for Webster resigned, and a caucus of Whigs voted to expel Tyler from the party in September 1841. When Webster informed Tyler that he would not resign, Tyler responded, "give me your hand on that, and now I will say to you that Henry Clay is a doomed man."
Facing a hostile Congress, Tyler and Webster turned their attention to foreign policy. The administration put a new emphasis on American influence in the Pacific Ocean, reaching the first U.S. treaty with China, seeking to partition Oregon Country with Britain, and announcing that the United States would oppose any attempt to colonize the Hawaiian Islands. The most pressing foreign policy issue involved United Kingdom–United States relations, relations with Britain, as the United States had nearly gone to war with Britain over the Caroline affair and a Aroostook War, border conflict between Maine and Canada. Seeking improved relations with the United States, British Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, Prime Minister Robert Peel dispatched Lord Ashburton on a special mission to the United States. After extensive negotiations, the United States and Britain reached the
Harrison extensively consulted Webster and Clay regarding presidential appointments, and the two Whig leaders competed to place their supporters and allies in key positions. Harrison initially hoped that Webster would serve as secretary of the treasury in order to spearhead his economic program, but Webster instead became United States Secretary of State, secretary of state, giving him oversight of foreign affairs. Just one month after taking office, Harrison died from pneumonia, and was succeeded by John Tyler. Though Tyler and Webster strongly differed regarding ideology (Tyler was a devotee of states' rights) and personality, they initially enjoyed a strong working relationship, partly because each saw Clay as a rival for power in the Whig Party. As Tyler, a former Democrat, had long been skeptical of the need for a national bank, Webster urged Whig congressmen to back a compromise bill put forward by Secretary of the Treasury Thomas Ewing which would have re-established the national bank but restricted its branching power. Congress rejected the compromise and instead passed Clay's bill, which was subsequently vetoed by Tyler. After Tyler vetoed another Whig bill, every Cabinet member except for Webster resigned, and a caucus of Whigs voted to expel Tyler from the party in September 1841. When Webster informed Tyler that he would not resign, Tyler responded, "give me your hand on that, and now I will say to you that Henry Clay is a doomed man."
Facing a hostile Congress, Tyler and Webster turned their attention to foreign policy. The administration put a new emphasis on American influence in the Pacific Ocean, reaching the first U.S. treaty with China, seeking to partition Oregon Country with Britain, and announcing that the United States would oppose any attempt to colonize the Hawaiian Islands. The most pressing foreign policy issue involved United Kingdom–United States relations, relations with Britain, as the United States had nearly gone to war with Britain over the Caroline affair and a Aroostook War, border conflict between Maine and Canada. Seeking improved relations with the United States, British Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, Prime Minister Robert Peel dispatched Lord Ashburton on a special mission to the United States. After extensive negotiations, the United States and Britain reached the Webster–Ashburton Treaty
The Webster–Ashburton Treaty, signed August 9, 1842, was a treaty that resolved several border issues between the United States and the British North American colonies (the region that became Canada). Signed under John Tyler's presidency, it r ...
, which clearly delineated Maine's northern border and other sections of the U.S.-Canada border that had been in dispute. Senator Thomas Hart Benton (politician), Thomas Hart Benton led Senate opposition to the treaty, arguing that it "needlessly and shamelessly" relinquished American territory, but few others joined Benton in voting against the treaty, and it won ratification.
After mid-1841, congressional Whigs continually pressured Webster to resign, and by early 1843, Tyler had also begun to pressure Webster to leave office. As Tyler moved even farther away from Whig positions and began preparing a campaign for the Democratic nomination in the 1844 U.S. presidential election, Webster left office in May 1843. With Webster gone, Tyler turned his attention to the Texas annexation. Clay was nominated for president at the 1844 Whig National Convention, while the Democrats spurned both Tyler and former President Van Buren in favor of James K. Polk, a protege of Andrew Jackson. Webster's service in the Tyler administration had badly damaged his credibility among Whigs, but he began to rebuild old alliances within the party. Tyler's attempts to annex Texas became the key issue in the 1844 election, and Webster came out strongly against annexation. He campaigned on behalf of Clay, telling one crowd, "I know of no great national constitutional question; I know of no great interest of the country ... in which there is any difference between the distinguished leader of the Whig Party and myself." Despite Webster's campaigning, Polk defeated Clay in a close election. The election of the expansionist Polk ensured the annexation of Texas, and annexation was completed after Polk took office.
Second period in the Senate
Polk administration, 1845–1849
Webster considered retiring from public office after the 1844 election, but he accepted election to the United States Senate in early 1845. Webster sought to block the adoption of Polk's domestic policies, but Congress, controlled by Democrats, reduced tariff rates through the Walker tariff and re-established the Independent Treasury system. In May 1846, the Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the 1 ...
began after Congress, responding to a Thornton Affair, clash instigated by U.S. troops against the Mexican Army at the disputed Texas–Mexico border, declared war on Mexico. During the war, Northern Whigs became increasingly split between "Conscience Whigs" like Charles Sumner, who strongly favored anti-slavery policies, and "Cotton Whigs" like Webster, who emphasized good relations with Southern leaders. Webster had been a long-standing opponent of slavery; in an 1837 speech he called slavery a "great moral, social, and political evil," and added that he would vote against "any thing that shall extend the slavery of the African race on this continent, or add other slaveholding states to the Union." But, unlike his more strongly anti-slavery constituents, he did not believe that Congress should interfere with slavery in the states, and he placed less emphasis on preventing the spread of slavery into the territories. Nonetheless, because Webster opposed the acquisition of Mexican territory (with the exception of San Francisco), he voted against the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, in which the United States acquired the Mexican Cession.
General Zachary Taylor's success in the Mexican–American War drove him to the front ranks of Whig candidates in the 1848 U.S. presidential election. As Taylor held unclear political positions and had never been publicly affiliated with the Whig Party, Clay and Webster each launched their own bids for the presidency, but opposition from the Conscience Whigs badly damaged Webster's standing. On the first ballot of the 1848 Whig National Convention Webster finished a distant fourth behind Taylor, Clay, and General Winfield Scott
Winfield Scott (June 13, 1786May 29, 1866) was an American military commander and political candidate. He served as a general in the United States Army from 1814 to 1861, taking part in the War of 1812, the Mexican–American War, the early s ...
. Taylor ultimately won the presidential nomination on the convention's third ballot, while Millard Fillmore
Millard Fillmore (January 7, 1800March 8, 1874) was the 13th president of the United States, serving from 1850 to 1853; he was the last to be a member of the Whig Party while in the White House. A former member of the U.S. House of Represen ...
of New York was selected as the party's vice presidential nominee. After Webster declined the request of Conscience Whigs to lead a new, anti-slavery third party, Conscience Whigs and "Barnburners and Hunkers, Barnburner" Democrats launched the Free Soil Party and nominated a ticket consisting of former President Van Buren and Charles Francis Adams Sr., Charles Francis Adams. Despite having previously stated that he would not support Taylor in the 1848 presidential campaign, Webster threw his backing behind Taylor. Ultimately, Taylor won the election, defeating both Van Buren and Democratic nominee Lewis Cass.
Taylor administration, 1849–1850
Having only tepidly endorsed Taylor's campaign, Webster was excluded from the new administration's Cabinet and was not consulted on major appointments. After the 1848 election, the fate of the territories acquired in the Mexican-American War became a major subject of debate in Congress, as Northern and Southern leaders quarreled over the extension of slavery. In January 1850, Clay introduced a plan which combined the major subjects under discussion. His legislative package included the admission of California as a free state, the State cessions, cession by Texas of some of its northern and western territorial claims in return for debt relief, the establishment of New Mexico Territory, New Mexico and Utah Territory, Utah territories, a ban on the importation of slaves into the District of Columbia for sale, and a more stringent fugitive slave law
The fugitive slave laws were laws passed by the United States Congress in 1793 and 1850 to provide for the return of enslaved people who escaped from one state into another state or territory. The idea of the fugitive slave law was derived from ...
. The plan faced opposition from strongly pro-slavery Southern leaders like Calhoun and anti-slavery Northerners like William Seward and Salmon Chase. President Taylor also opposed Clay's proposal, since he favored granting California statehood immediately and denied the legitimacy of Texas's claims over New Mexico.
Clay had won Webster's backing for his proposal before presenting it to Congress, and Webster provided strong support for Clay's bill in the Senate. In a speech that became known as the "Seventh of March" speech, Webster attacked Northerners and Southerners alike for stirring up tensions over slavery. He admonished Northerners for obstructing the return of Fugitive slaves in the United States, fugitive slaves but attacked Southern leaders for openly contemplating secession. After the speech, Webster was bitterly attacked by New England Abolitionism in the United States, abolitionists. Theodore Parker complained, "No living man has done so much to debauch the conscience of the nation," while Horace Mann described Webster as "a fallen star! Lucifer descending from Heaven!" In contrast to that view, James G. Blaine wrote a few decades later:
The debate over Clay's compromise proposal continued into July 1850, when Taylor suddenly and unexpectedly died of an illness.
Secretary of State in the Fillmore administration
Compromise of 1850
 Millard Fillmore ascended to the presidency upon Taylor's death. Shortly after taking office, Fillmore dismissed Taylor's Cabinet appointees, named Webster as his secretary of state, and came out in favor of Clay's compromise. Fillmore chose the remaining members of his Cabinet in consultation with Webster, and Webster became the unofficial leader in the Cabinet. After Fillmore took office, Clay took a temporary leave from the Senate, but Democratic Senator Stephen A. Douglas of Illinois took the lead in advocating for a compromise based largely on Clay's proposals. On behalf of the president, Webster drafted a special message to Congress calling for an end to the crisis over the territories, and he used the power of patronage to woo potential supporters. Soon after the Fillmore administration delivered the special message, Congress passed Douglas's legislative package, which became known as the
Millard Fillmore ascended to the presidency upon Taylor's death. Shortly after taking office, Fillmore dismissed Taylor's Cabinet appointees, named Webster as his secretary of state, and came out in favor of Clay's compromise. Fillmore chose the remaining members of his Cabinet in consultation with Webster, and Webster became the unofficial leader in the Cabinet. After Fillmore took office, Clay took a temporary leave from the Senate, but Democratic Senator Stephen A. Douglas of Illinois took the lead in advocating for a compromise based largely on Clay's proposals. On behalf of the president, Webster drafted a special message to Congress calling for an end to the crisis over the territories, and he used the power of patronage to woo potential supporters. Soon after the Fillmore administration delivered the special message, Congress passed Douglas's legislative package, which became known as the Compromise of 1850
The Compromise of 1850 was a package of five separate bills passed by the United States Congress in September 1850 that defused a political confrontation between slave and free states on the status of territories acquired in the Mexican–Am ...
.
Due to a prosperous economy and various other trends, few Whigs pushed for a revival of the national bank and other long-standing party policies during the Fillmore administration, and the Compromise of 1850 became the central political issue. While Fillmore hoped to reconcile with anti-Compromise Northern Whigs, Webster sought to purge them from the party, and he frequently intervened to block the election or appointment of anti-Compromise Whigs. In the North, the most controversial portion of the Compromise of 1850 was the Fugitive Slave Act of 1850, and Webster became closely involved in enforcing the law. Disputes over fugitive slaves were widely publicized North and South, inflaming passions and raising tensions in the aftermath of the Compromise of 1850. Many of the administration's prosecutions or attempts to return slaves ended badly for the government, as in the case of Shadrach Minkins. In Massachusetts, anti-slavery Whigs allied with Democrats and, in a major rebuke to Webster, elected Free Soil leader Charles Sumner to the Senate.
Opening of the New York & Erie Rail Road
When the Erie Railroad, New York & Erie Rail Road was completed in May 1851, President Fillmore and several members of his cabinet, including Webster, made a special, two-day excursion run to open the railway. It is reported that Webster viewed the entire run from a rocking chair attached to a flatcar, with a steamer rug and jug of high-quality Medford, Massachusetts, Medford rum. At stops, he would get down and speechify.
Foreign affairs
Fillmore appointed Webster not only for his national stature and pro-Compromise position, but also for his experience in foreign affairs, and Fillmore relied on Webster to guide his administration's foreign policy. In the aftermath of the failed Hungarian Revolution of 1848, a diplomatic incident with the Austrian Empire arose over the Taylor administration's sympathetic actions towards the Hungarian rebels. Rather than backing down, the Fillmore administration secured the release of exiled Hungarian leader Lajos Kossuth from the Ottoman Empire and gave a banquet in Kossuth's honor. In 1851, Webster wrote a book about Kossuth's life.
1852 election
 Encouraged by Fillmore's professed lack of desire to pursue the Whig nomination in the
Encouraged by Fillmore's professed lack of desire to pursue the Whig nomination in the 1852 U.S. presidential election
The 1852 United States presidential election was the 17th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 2, 1852. Democrat Franklin Pierce defeated Whig nominee General Winfield Scott.
Incumbent Whig President Millard Fillmore ha ...
, Webster launched another campaign for the presidency in 1851. Fillmore was sympathetic to the ambitions of his secretary of state, but he was unwilling to completely rule out accepting the party's 1852 nomination, as he feared doing so would allow his rival, William Seward, to gain control of the party. Another candidate emerged in the form of General Winfield Scott, who, like previously successful Whig presidential nominees William Henry Harrison and Zachary Taylor, had earned fame for his martial accomplishments. Scott had supported the Compromise of 1850, but his association with Seward made him unacceptable to Southern Whigs. As Southerners retained a lingering distrust of Webster, they threw their backing behind Fillmore. Thus, Scott emerged as the preferred candidate of most Northern Whigs, Fillmore became the main candidate of Southern Whigs, and Webster was only able to win backing from a handful of delegates, most of whom were from New England.
On the first presidential ballot of the 1852 Whig National Convention, Fillmore received 133 of the necessary 147 votes, while Scott won 131 and Webster won 29. Although both Webster and Fillmore were willing to withdraw in favor of the other, their respective delegates at the convention were unable to unite around one candidate, and Scott took the nomination on the 53rd ballot. Webster was personally devastated by the defeat, and he refused to endorse Scott's candidacy. Webster allowed various third party groups to nominate him for president, although he did not openly condone these efforts. Scott proved to be a poor candidate, and he suffered the worst defeat in Whig history, losing to Democratic nominee Franklin Pierce. Thousands of anti-Scott Whigs and members of the Nativism (politics), nativist Know Nothing, Native American Party cast their vote for Webster.
Personal life, family, and religious views
 In 1808, Webster married Grace Fletcher, a schoolteacher and the daughter of a New Hampshire clergyman. Between 1810 and 1822, Daniel and Grace had five children: Grace, Fletcher Webster, Daniel "Fletcher", Julia, Edward, and Charles. Grace and Charles died before reaching adulthood. Webster's wife, Grace, died in January 1828 due to a cancerous tumor, and Webster suffered another loss when his brother, Ezekiel, died in April 1829. In December 1829, Webster married Caroline LeRoy, the 32-year-old daughter of a New York merchant. They remained married until Webster's death, and she lived until 1882. She and Webster had two children together, another daughter named Grace and a son named Noah Webster. After the death of his first wife, Webster was frequently the subject of rumors in Washington regarding his alleged promiscuity; many suspected that the painter Sarah Goodridge, with whom he had a close relationship, was his mistress.
Webster and his family lived in Portsmouth until 1816 when they relocated to Boston. In 1831, Webster purchased a 150-acre estate (now known as the Thomas–Webster Estate) in Marshfield, Massachusetts. In the ensuing years, Webster spent much of his earnings making various improvements to his estate, and he made it his primary residence in 1837. After 1829, Webster also owned his father's home, Daniel Webster Family Home, The Elms, in Franklin, New Hampshire. Webster's older son, Fletcher, married a niece of Joseph Story, established a profitable law practice, served as Chief Clerk (United States Department of State), chief clerk of the State Department, and was the only one of his siblings to outlive his father. Fletcher died at the 1862 Second Battle of Bull Run while serving as a colonel in the Union (American Civil War), Union army. Webster's younger son, Edward, died of typhoid fever in January 1848 while serving in the Mexican-American War. Webster's daughter, Julia, married Samuel Appleton Appleton, but died of tuberculosis in April 1848.
Conflicting opinions have been voiced as to his religion. The Unitarianism, Unitarian Universalist Church, citing ''Unitarianism in America'' from 1902, claim him as their own. Another source, the 1856 biography ''The American Statesman: The Life and Character of Daniel Webster'', proclaims him an avowed orthodox Trinitarian, baptized and raised in an Orthodox Congregational Church, and who died a member of the Episcopal Church. Remini writes that, though Webster occasionally attended other churches, he remained closely affiliated with the Congregational church throughout his life. In an 1807 letter to a Congregational pastor, Webster wrote, "I believe in the utter inability of any human being to work out his own Salvation, without the constant aids of the spirit of all grace. ... Although I have great respect for some other forms of worship, I believe the Congregational mode, on the whole, to be preferable to any other."
In 1808, Webster married Grace Fletcher, a schoolteacher and the daughter of a New Hampshire clergyman. Between 1810 and 1822, Daniel and Grace had five children: Grace, Fletcher Webster, Daniel "Fletcher", Julia, Edward, and Charles. Grace and Charles died before reaching adulthood. Webster's wife, Grace, died in January 1828 due to a cancerous tumor, and Webster suffered another loss when his brother, Ezekiel, died in April 1829. In December 1829, Webster married Caroline LeRoy, the 32-year-old daughter of a New York merchant. They remained married until Webster's death, and she lived until 1882. She and Webster had two children together, another daughter named Grace and a son named Noah Webster. After the death of his first wife, Webster was frequently the subject of rumors in Washington regarding his alleged promiscuity; many suspected that the painter Sarah Goodridge, with whom he had a close relationship, was his mistress.
Webster and his family lived in Portsmouth until 1816 when they relocated to Boston. In 1831, Webster purchased a 150-acre estate (now known as the Thomas–Webster Estate) in Marshfield, Massachusetts. In the ensuing years, Webster spent much of his earnings making various improvements to his estate, and he made it his primary residence in 1837. After 1829, Webster also owned his father's home, Daniel Webster Family Home, The Elms, in Franklin, New Hampshire. Webster's older son, Fletcher, married a niece of Joseph Story, established a profitable law practice, served as Chief Clerk (United States Department of State), chief clerk of the State Department, and was the only one of his siblings to outlive his father. Fletcher died at the 1862 Second Battle of Bull Run while serving as a colonel in the Union (American Civil War), Union army. Webster's younger son, Edward, died of typhoid fever in January 1848 while serving in the Mexican-American War. Webster's daughter, Julia, married Samuel Appleton Appleton, but died of tuberculosis in April 1848.
Conflicting opinions have been voiced as to his religion. The Unitarianism, Unitarian Universalist Church, citing ''Unitarianism in America'' from 1902, claim him as their own. Another source, the 1856 biography ''The American Statesman: The Life and Character of Daniel Webster'', proclaims him an avowed orthodox Trinitarian, baptized and raised in an Orthodox Congregational Church, and who died a member of the Episcopal Church. Remini writes that, though Webster occasionally attended other churches, he remained closely affiliated with the Congregational church throughout his life. In an 1807 letter to a Congregational pastor, Webster wrote, "I believe in the utter inability of any human being to work out his own Salvation, without the constant aids of the spirit of all grace. ... Although I have great respect for some other forms of worship, I believe the Congregational mode, on the whole, to be preferable to any other."
Death
By early 1852, Webster had begun to suffer from cirrhosis of the liver, and his poor health increasingly made it difficult for him to serve as secretary of state. In September 1852, Webster returned to his Marshfield estate, where his health continued to decline due to cirrhosis and a subdural hematoma. He died at Marshfield on October 24, 1852, and is buried in Winslow Cemetery near his estate. His last words were: "I still live."
Legacy
Historical evaluations
Remini writes that "whether men hated or admired [Webster], all agreed ... on the majesty of his oratory, the immensity of his intellectual powers, and the primacy of his constitutional knowledge." Ralph Waldo Emerson, who had criticized Webster following the Seventh of March address, remarked in the immediate aftermath of his death that Webster was "the completest man", and that "nature had not in our days, or not since Napoleon I of France, Napoleon, cut out such a masterpiece." In ''Profiles in Courage'', John F. Kennedy called Webster's defense of the Compromise of 1850, despite the risk to his presidential ambitions and the denunciations he faced from the North, one of the "greatest acts of courageous principle" in the history of the Senate. Conversely, ''Seventh of March'' has been criticized by Henry Cabot Lodge who contrasted the speech's support of the 1850 compromise with his 1833 rejection of similar measures. "While he was brave and true and wise in 1833," said Lodge, "in 1850 he was not only inconsistent, but that he erred deeply in policy and statesmanship" in his advocacy of a policy that "made war inevitable by encouraging slave-holders to believe that they could always obtain anything they wanted by a sufficient show of violence."
Several historians suggest Webster failed to exercise leadership for any political issue or vision. Lodge describes Webster's "susceptibility to outside influences that formed such an odd trait in the character of a man so imperious by nature. When acting alone, he spoke his own opinions. When in a situation where public opinion was concentrated against him, he submitted to modifications of his views with a curious and indolent indifference." Similarly, Arthur M. Schlesinger Jr., Arthur Schlesinger cites Webster's letter requesting retainers for fighting for the national bank, one of his most inveterate causes; he then asks how Webster could "expect the American people to follow him through hell or high water when he would not lead unless someone made up a purse for him?" Remini writes that "Webster was a thoroughgoing elitist—and he reveled in it."
Webster retains his high prestige in some recent historiography. Baxter argues that his nationalistic view of the union as one and inseparable from liberty helped the union to triumph over the states-rights Confederacy, making it his greatest contribution. In 1959, the Senate named Webster, Clay, Calhoun, Robert M. La Follette, and Robert A. Taft as the five greatest senators in history. However Bartlett, emphasizing Webster's private life, says his great oratorical achievements were in part undercut by his improvidence with money, his excessively opulent lifestyle, and his numerous conflict of interest situations. Remini points out that Webster's historical orations taught Americans their history before textbooks were widely available.
While evaluations on his political career vary, Webster is widely praised for his talent as an orator and attorney. Former Solicitor General of the United States, Solicitor General Seth P. Waxman writes that "in the realm of advocacy, Webster doesn't merely sit in the Pantheon: He is Zeus himself." Kennedy praised Webster's "ability to make alive and supreme the latent sense of oneness, of union, that all Americans felt but few could express."[Allan Nevins, ''Ordeal of the Union'' (1947) 1:288.] Schlesinger, however, notes that he is also an example of the limitations of formal oratory: Congress heard Webster or Clay with admiration, but they rarely prevailed at the vote. Plainer speech and party solidarity were more effective, and Webster never approached Jackson's popular appeal.
Memorials
 Webster's legacy has been commemorated by numerous means, including the Daniel Webster Highway and Mount Webster in New Hampshire. His statue stands in the National Statuary Hall Collection, while another Statue of Daniel Webster (New York City), statue stands in Central Park. The ''USS Daniel Webster (SSBN-626)'' and the ''SS Daniel Webster'' were both named for Webster. The first Webster postage stamp was issued in 1870. In all, Daniel Webster is honored on 14 different US postage issues, more than most U.S. Presidents.
Webster's legacy has been commemorated by numerous means, including the Daniel Webster Highway and Mount Webster in New Hampshire. His statue stands in the National Statuary Hall Collection, while another Statue of Daniel Webster (New York City), statue stands in Central Park. The ''USS Daniel Webster (SSBN-626)'' and the ''SS Daniel Webster'' were both named for Webster. The first Webster postage stamp was issued in 1870. In all, Daniel Webster is honored on 14 different US postage issues, more than most U.S. Presidents.[Scotts US Stamp Catalogue] There are 27 towns named for Webster in California, Webster,_Florida, Florida, Webster,_Illinois, Illinois, Webster,_Indiana, Indiana, Webster,_Iowa, Iowa, Webster,_Kansas, Kansas, Webster,_Kentucky, Kentucky, Webster,_Maine, Maine, Webster,_Massachusetts, Massachusetts, Webster,_Michigan, Michigan, Webster,_Minnesota, Minnesota, Webster,_Nebraska, Nebraska, Webster,_New Hampshire, New Hampshire, Webster,_New York, New York, Webster,_North Carolina, North Carolina, Webster,_North Dakota, North Dakota, Webster,_Ohio, Ohio, Webster,_Pennsylvania, Pennsylvania, Webster,_South Dakota, South Dakota, Webster,_Texas, Texas, Webster,_Virginia, Virginia, and Webster,_West Virginia, West Virginia, including two in Wisconsin (Webster, Burnett County, Wisconsin, Webster, Burnett County and Webster, Vernon County, Wisconsin, Webster, Vernon County), a ghost town in Colorado, and Webster and Webster Hollow in Tennessee. Seven County (United States), counties or List of parishes in Louisiana, parishes are named for Webster.
In media
Webster is the major character in a fictional short story, ''The Devil and Daniel Webster'', by Stephen Vincent Benét. It serves as the basis for a one-act opera of the same name written by American composer Douglas Moore.
Webster is briefly discussed in Chapter XIX of MacKinlay Kantor's Pulitzer Prize-winning novel "Andersonville" (1955).
On film, Webster has been portrayed by
* George MacQuarrie in ''The Mighty Barnum'' (1934)
* Sidney Toler in ''The Gorgeous Hussy'' (1936)
* Emmett Vogan in ''The Monroe Doctrine'' (1939)
* Harry Humphries in ''Abe Lincoln in Illinois (film), Abe Lincoln in Illinois'' (1940)
* Edward Arnold (actor), Edward Arnold in ''The Devil and Daniel Webster (film), The Devil and Daniel Webster'' (1941)
* Anthony Hopkins in ''Shortcut to Happiness'' (2007)
See also
* List of deaths through alcohol
* Origins of the American Civil War
* Webster/Sainte-Laguë method
Notes
References
Works cited
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
Biographies
* Irving H. Bartlett, Bartlett, Irving H. ''Daniel Webster'' (1978
online edition
* Baxter, Maurice G. "Webster, Daniel"; ''American National Biography Online'' Feb. 2000. online edition at academic libraries
* Baxter, Maurice G. ''One and Inseparable: Daniel Webster and the Union.'' (1984).
*
* Current, Richard Nelson. ''Daniel Webster and the Rise of National Conservatism'' (1955), short biography
* Curtis, George Ticknor. ''Life of Daniel Webster'' (1870), useful for quotation
online edition vol 1online edition vol 2
* Claude Fuess, Fuess, Claude Moore ''Daniel Webster.'' (2 vols. 1930). scholarly biography
* Remini, Robert V. ''Daniel Webster: The Man and His Time'' (1997)
* Ogg, Frederic Austin. ''Daniel Webster'' (1914
online edition
old scholarly biography
* Peterson, Merrill D. ''The Great Triumvirate: Webster, Clay, and Calhoun'' (1983)
Specialized scholarly studies
* Arntson, Paul, and Craig R. Smith. "The Seventh of March Address: A Mediating Influence." ''Southern Speech Communication Journal'' 40 (Spring 1975): 288–301.
* Bartlett, Irving H. "Daniel Webster as a Symbolic Hero." ''New England Quarterly'' 45 (December 1972): 484–507
in JSTOR
* Baxter, Maurice G. ''Daniel Webster and the Supreme Court'' (1966)
* Birkner, Michael. "Daniel Webster and the Crisis of Union, 1850." ''Historical New Hampshire'' 37 (Summer/Fall 1982): 151–73.
* Brauer, Kinley J. "The Webster-Lawrence Feud: A Study in Politics and Ambitions." ''Historian'' 29 (November 1966): 34–59.
* Brown, Thomas. "Daniel Webster: Conservative Whig." In ''Politics and Statesmanship: Essays on the American Whig Party'', (1985) pp. 49–92
online
* Carey, Robert Lincoln. ''Daniel Webster as an Economist.'' (1929)
online edition
* Dalzell, Robert F. Jr. ''Daniel Webster and the Trial of American Nationalism, 1843–1852.'' (1973).
* Dubofsky, Melvyn. "Daniel Webster and the Whig Theory of Economic Growth: 1828–1848." ''New England Quarterly'' 42 (December 1969): 551–72
in JSTOR
* Eisenstadt, Arthur A. "Daniel Webster and the Seventh of March." ''Southern Speech Journal'' 20 (Winter 1954): 136–47.
* Fields, Wayne. "The Reply to Hayne: Daniel Webster and the Rhetoric of Stewardship." ''Political Theory'' 11 (February 1983): 5–28
in JSTOR
* Foster, Herbert D. "Webster's Seventh of March Speech and the Secession Movement, 1850." ''American Historical Review'' 27 (January 1922): 245–70
in JSTOR
* Formisano, Ronald P. ''The Transformation of Political Culture: Massachusetts Parties, 1790s–1840s'' (1983)
* Jones, Howard. ''To the Webster–Ashburton Treaty: A Study in Anglo-American Relations, 1783–1843.'' (1977). 251 pp.
* Nathans, Sydney. ''Daniel Webster and Jacksonian Democracy.'' (1973).
* Nathans, Sydney. "Daniel Webster, Massachusetts Man," ''New England Quarterly'' 39 (June 1966): 161–81
in JSTOR
* Nevins, Allan. ''Ordeal of the Union: Fruits of Manifest Destiny, 1847–1852'' (1947), highly detailed narrative of national politics.
* Parish, Peter J. "Daniel Webster, New England, and the West." ''Journal of American History'' 54 (December 1967): 524–49
in JSTOR
* Prince, Carl E., and Seth Taylor. "Daniel Webster, the Boston Associates, and the U.S. Government's Role in the Industrializing Process, 1815–1830." ''Journal of the Early Republic'' 2 (Fall 1982): 283–99
in JSTOR
* Rakestraw, Donald A. ''Daniel Webster: Defender of Peace.'' Lanham, MD: Rowman and Littlefield, 2018.
* Shade, William G. "The Second Party System" in Paul Kleppner ed., ''Evolution of American Electoral Systems'' (1983)
* Sheidley, Harlow W. "The Webster–Hayne Debate: Recasting New England's Sectionalism." ''New England Quarterly'' 1994 67(1): 5–29
in Jstor
* Sheidley, Harlow W. "'Congress only can declare war' and 'the President is Commander in Chief': Daniel Webster and the War Power." ''Diplomatic History'' 12 (Fall 1988): 383–409.
* Shewmaker, Kenneth E. "Forging the 'Great Chain': Daniel Webster and the Origins of American Foreign Policy toward East Asia and the Pacific, 1841–1852." ''Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society'' 129 (September 1985): 225–59.
* Shewmaker, Kenneth E. ed. ''Daniel Webster: "The Completest Man.'' (1990), specialized studies by scholars
* Simpson, Brooks D. "Daniel Webster and the Cult of the Constitution," ''Journal of American Culture'' 15 (Spring 1992): 15–23. online in Blackwell Synergy
* Smith, Craig R. "Daniel Webster's Epideictic Speaking: A Study in Emerging Whig Virtues
online edition
* Smith, Craig R. ''Daniel Webster and the Oratory of Civil Religion.'' (2005) 300pp
* Smith, Craig R. "Daniel Webster's July 17th Address: A Mediating Influence in the 1850 Compromise," ''Quarterly Journal of Speech'' 71 (August 1985): 349–61.
* Smith, Craig R. ''Defender of the Union: The Oratory of Daniel Webster.'' (1989).
* Szasz, Ferenc M. "Daniel Webster – Architect of America's 'Civil Religion'," ''Historical New Hampshire'' 34 (Fall/Winter 1979): 223–43.
* Wilson, Major L. "Of Time and the Union: Webster and His Critics in the Crisis of 1850." ''Civil War History'' 14 (December 1968): 293–306. ch 1 of Wilson, ''Space, Time, and Freedom: The Quest for Nationality and the Irrepressible Conflict, 1815–1861'' (1974
online edition
Primary sources
* ''Select Speeches of Daniel Webster 1817–1845'' edited by A. J. George, (1903
Contains: Defence of the Kennistons; The Dartmouth College Case; First Settlement of New England; The Bunker Hill Monument; The Reply to Hayne; The Murder of Captain Joseph White; The Constitution Not a Compact Between Sovereign States; Speech at Saratoga; and Eulogy on Mr. Justice Story.
* ''The works of Daniel Webster'' edited in 6 vol. by Edward Everett, Boston: Little, Brown and company, 1853
online edition
* McIntyre, J. W., ed. ''The Writings and Speeches of Daniel Webster''. 18 vols. (1903)
vol 8 online
* Tefft, B. F., ed. ''The Speeches of Daniel Webster and His Master-Pieces''. Alta ed. Philadelphia, Penn.: Porter and Coates, 1854.
* Van Tyne, Claude H., ed. ''The Letters of Daniel Webster, from Documents Owned Principally by the New Hampshire Historical Society'' (1902)
online edition
* Webster, Fletcher, ed. ''The Private Correspondence of Daniel Webster.'' 2 vols. 1857
online edition vol 1
* Wiltse, Charles M., Harold D. Moser, and Kenneth E. Shewmaker (Diplomatic papers), eds., ''The Papers of Daniel Webster'', (1974–1989). Published for Dartmouth College by the University Press of New England. ser. 1. Correspondence: v. 1. 1798–1824. v. 2. 1825–1829. v. 3. 1830–1834. v. 4. 1835–1839. v. 5. 1840–1843. v. 6. 1844–1849. v. 7. 1850–1852ser. 2. Legal papers: v. 1. The New Hampshire practice. v. 2. The Boston practice. v. 3. The federal practice (2 v.) – ser. 3. Diplomatic papers: v. 1. 1841–1843. v. 2. 1850–1852ser. 4. Speeches and formal writings: v. 1. 1800–1833. v. 2. 1834–1852.
External links
Daniel Webster Estate
from the Library of Congress
*
*
''The works of Daniel Webster...'' 6 vol, 1853 edition
''The private correspondence of Daniel Webster'' ed. by Fletcher Webster. 2v 1857 editionPortrait of Daniel Webster
painted by William Willard (painter), William Willard circa 1839–1985
Daniel Webster Speeches Collection
from the University of Missouri Division of Special Collections and Rare Books
, -
, -
, -
, -
, -
, -
, -
{{DEFAULTSORT:Webster, Daniel
1782 births
1852 deaths
People from Salisbury, New Hampshire
American people of English descent
United States Secretaries of State
William Henry Harrison administration cabinet members
Tyler administration cabinet members
Fillmore administration cabinet members
Federalist Party members of the United States House of Representatives from New Hampshire
Federalist Party members of the United States House of Representatives from Massachusetts
National Republican Party members of the United States House of Representatives from Massachusetts
National Republican Party United States senators from Massachusetts
Whig Party United States senators from Massachusetts
Whig Party (United States) presidential nominees
New Hampshire National Republicans
New Hampshire Whigs
Massachusetts Whigs
Candidates in the 1836 United States presidential election
Candidates in the 1848 United States presidential election
Candidates in the 1852 United States presidential election
Great Triumvirate
American political party founders
Philhellenes
People from Franklin, New Hampshire
People from Fryeburg, Maine
People from Boscawen, New Hampshire
American colonization movement
Fryeburg Academy alumni
Phillips Exeter Academy alumni
Dartmouth College alumni
Fellows of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences
Members of the American Antiquarian Society
Hall of Fame for Great Americans inductees
Webster County, Georgia
Deaths from cirrhosis
Deaths from subdural hematoma
Neurological disease deaths in Massachusetts
Alcohol-related deaths in Massachusetts
Burials at Winslow Cemetery
American nationalists
 He remained politically active during his time out of Congress, serving as a
He remained politically active during his time out of Congress, serving as a  At the behest of Federalist leaders and the business elite in Boston, Webster agreed to run for the United States House of Representatives in 1822. He won the election and returned to Congress in December 1823. In recognition of his mastery of legal issues, Speaker of the House Henry Clay assigned him the chairmanship of the House Judiciary Committee. In that role, he tried to pass a bill that would relieve Supreme Court justices of having to travel to far-flung western districts, but his bill did not receive a vote in the House. Seeking to re-establish his reputation for oratorical prowess on the floor of the House of Representatives, he gave a speech supporting the
At the behest of Federalist leaders and the business elite in Boston, Webster agreed to run for the United States House of Representatives in 1822. He won the election and returned to Congress in December 1823. In recognition of his mastery of legal issues, Speaker of the House Henry Clay assigned him the chairmanship of the House Judiciary Committee. In that role, he tried to pass a bill that would relieve Supreme Court justices of having to travel to far-flung western districts, but his bill did not receive a vote in the House. Seeking to re-establish his reputation for oratorical prowess on the floor of the House of Representatives, he gave a speech supporting the 
 Harrison extensively consulted Webster and Clay regarding presidential appointments, and the two Whig leaders competed to place their supporters and allies in key positions. Harrison initially hoped that Webster would serve as secretary of the treasury in order to spearhead his economic program, but Webster instead became United States Secretary of State, secretary of state, giving him oversight of foreign affairs. Just one month after taking office, Harrison died from pneumonia, and was succeeded by John Tyler. Though Tyler and Webster strongly differed regarding ideology (Tyler was a devotee of states' rights) and personality, they initially enjoyed a strong working relationship, partly because each saw Clay as a rival for power in the Whig Party. As Tyler, a former Democrat, had long been skeptical of the need for a national bank, Webster urged Whig congressmen to back a compromise bill put forward by Secretary of the Treasury Thomas Ewing which would have re-established the national bank but restricted its branching power. Congress rejected the compromise and instead passed Clay's bill, which was subsequently vetoed by Tyler. After Tyler vetoed another Whig bill, every Cabinet member except for Webster resigned, and a caucus of Whigs voted to expel Tyler from the party in September 1841. When Webster informed Tyler that he would not resign, Tyler responded, "give me your hand on that, and now I will say to you that Henry Clay is a doomed man."
Facing a hostile Congress, Tyler and Webster turned their attention to foreign policy. The administration put a new emphasis on American influence in the Pacific Ocean, reaching the first U.S. treaty with China, seeking to partition Oregon Country with Britain, and announcing that the United States would oppose any attempt to colonize the Hawaiian Islands. The most pressing foreign policy issue involved United Kingdom–United States relations, relations with Britain, as the United States had nearly gone to war with Britain over the Caroline affair and a Aroostook War, border conflict between Maine and Canada. Seeking improved relations with the United States, British Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, Prime Minister Robert Peel dispatched Lord Ashburton on a special mission to the United States. After extensive negotiations, the United States and Britain reached the
Harrison extensively consulted Webster and Clay regarding presidential appointments, and the two Whig leaders competed to place their supporters and allies in key positions. Harrison initially hoped that Webster would serve as secretary of the treasury in order to spearhead his economic program, but Webster instead became United States Secretary of State, secretary of state, giving him oversight of foreign affairs. Just one month after taking office, Harrison died from pneumonia, and was succeeded by John Tyler. Though Tyler and Webster strongly differed regarding ideology (Tyler was a devotee of states' rights) and personality, they initially enjoyed a strong working relationship, partly because each saw Clay as a rival for power in the Whig Party. As Tyler, a former Democrat, had long been skeptical of the need for a national bank, Webster urged Whig congressmen to back a compromise bill put forward by Secretary of the Treasury Thomas Ewing which would have re-established the national bank but restricted its branching power. Congress rejected the compromise and instead passed Clay's bill, which was subsequently vetoed by Tyler. After Tyler vetoed another Whig bill, every Cabinet member except for Webster resigned, and a caucus of Whigs voted to expel Tyler from the party in September 1841. When Webster informed Tyler that he would not resign, Tyler responded, "give me your hand on that, and now I will say to you that Henry Clay is a doomed man."
Facing a hostile Congress, Tyler and Webster turned their attention to foreign policy. The administration put a new emphasis on American influence in the Pacific Ocean, reaching the first U.S. treaty with China, seeking to partition Oregon Country with Britain, and announcing that the United States would oppose any attempt to colonize the Hawaiian Islands. The most pressing foreign policy issue involved United Kingdom–United States relations, relations with Britain, as the United States had nearly gone to war with Britain over the Caroline affair and a Aroostook War, border conflict between Maine and Canada. Seeking improved relations with the United States, British Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, Prime Minister Robert Peel dispatched Lord Ashburton on a special mission to the United States. After extensive negotiations, the United States and Britain reached the  Millard Fillmore ascended to the presidency upon Taylor's death. Shortly after taking office, Fillmore dismissed Taylor's Cabinet appointees, named Webster as his secretary of state, and came out in favor of Clay's compromise. Fillmore chose the remaining members of his Cabinet in consultation with Webster, and Webster became the unofficial leader in the Cabinet. After Fillmore took office, Clay took a temporary leave from the Senate, but Democratic Senator Stephen A. Douglas of Illinois took the lead in advocating for a compromise based largely on Clay's proposals. On behalf of the president, Webster drafted a special message to Congress calling for an end to the crisis over the territories, and he used the power of patronage to woo potential supporters. Soon after the Fillmore administration delivered the special message, Congress passed Douglas's legislative package, which became known as the
Millard Fillmore ascended to the presidency upon Taylor's death. Shortly after taking office, Fillmore dismissed Taylor's Cabinet appointees, named Webster as his secretary of state, and came out in favor of Clay's compromise. Fillmore chose the remaining members of his Cabinet in consultation with Webster, and Webster became the unofficial leader in the Cabinet. After Fillmore took office, Clay took a temporary leave from the Senate, but Democratic Senator Stephen A. Douglas of Illinois took the lead in advocating for a compromise based largely on Clay's proposals. On behalf of the president, Webster drafted a special message to Congress calling for an end to the crisis over the territories, and he used the power of patronage to woo potential supporters. Soon after the Fillmore administration delivered the special message, Congress passed Douglas's legislative package, which became known as the  Encouraged by Fillmore's professed lack of desire to pursue the Whig nomination in the
Encouraged by Fillmore's professed lack of desire to pursue the Whig nomination in the 
 In 1808, Webster married Grace Fletcher, a schoolteacher and the daughter of a New Hampshire clergyman. Between 1810 and 1822, Daniel and Grace had five children: Grace, Fletcher Webster, Daniel "Fletcher", Julia, Edward, and Charles. Grace and Charles died before reaching adulthood. Webster's wife, Grace, died in January 1828 due to a cancerous tumor, and Webster suffered another loss when his brother, Ezekiel, died in April 1829. In December 1829, Webster married Caroline LeRoy, the 32-year-old daughter of a New York merchant. They remained married until Webster's death, and she lived until 1882. She and Webster had two children together, another daughter named Grace and a son named Noah Webster. After the death of his first wife, Webster was frequently the subject of rumors in Washington regarding his alleged promiscuity; many suspected that the painter Sarah Goodridge, with whom he had a close relationship, was his mistress.
Webster and his family lived in Portsmouth until 1816 when they relocated to Boston. In 1831, Webster purchased a 150-acre estate (now known as the Thomas–Webster Estate) in Marshfield, Massachusetts. In the ensuing years, Webster spent much of his earnings making various improvements to his estate, and he made it his primary residence in 1837. After 1829, Webster also owned his father's home, Daniel Webster Family Home, The Elms, in Franklin, New Hampshire. Webster's older son, Fletcher, married a niece of Joseph Story, established a profitable law practice, served as Chief Clerk (United States Department of State), chief clerk of the State Department, and was the only one of his siblings to outlive his father. Fletcher died at the 1862 Second Battle of Bull Run while serving as a colonel in the Union (American Civil War), Union army. Webster's younger son, Edward, died of typhoid fever in January 1848 while serving in the Mexican-American War. Webster's daughter, Julia, married Samuel Appleton Appleton, but died of tuberculosis in April 1848.
Conflicting opinions have been voiced as to his religion. The Unitarianism, Unitarian Universalist Church, citing ''Unitarianism in America'' from 1902, claim him as their own. Another source, the 1856 biography ''The American Statesman: The Life and Character of Daniel Webster'', proclaims him an avowed orthodox Trinitarian, baptized and raised in an Orthodox Congregational Church, and who died a member of the Episcopal Church. Remini writes that, though Webster occasionally attended other churches, he remained closely affiliated with the Congregational church throughout his life. In an 1807 letter to a Congregational pastor, Webster wrote, "I believe in the utter inability of any human being to work out his own Salvation, without the constant aids of the spirit of all grace. ... Although I have great respect for some other forms of worship, I believe the Congregational mode, on the whole, to be preferable to any other."
In 1808, Webster married Grace Fletcher, a schoolteacher and the daughter of a New Hampshire clergyman. Between 1810 and 1822, Daniel and Grace had five children: Grace, Fletcher Webster, Daniel "Fletcher", Julia, Edward, and Charles. Grace and Charles died before reaching adulthood. Webster's wife, Grace, died in January 1828 due to a cancerous tumor, and Webster suffered another loss when his brother, Ezekiel, died in April 1829. In December 1829, Webster married Caroline LeRoy, the 32-year-old daughter of a New York merchant. They remained married until Webster's death, and she lived until 1882. She and Webster had two children together, another daughter named Grace and a son named Noah Webster. After the death of his first wife, Webster was frequently the subject of rumors in Washington regarding his alleged promiscuity; many suspected that the painter Sarah Goodridge, with whom he had a close relationship, was his mistress.
Webster and his family lived in Portsmouth until 1816 when they relocated to Boston. In 1831, Webster purchased a 150-acre estate (now known as the Thomas–Webster Estate) in Marshfield, Massachusetts. In the ensuing years, Webster spent much of his earnings making various improvements to his estate, and he made it his primary residence in 1837. After 1829, Webster also owned his father's home, Daniel Webster Family Home, The Elms, in Franklin, New Hampshire. Webster's older son, Fletcher, married a niece of Joseph Story, established a profitable law practice, served as Chief Clerk (United States Department of State), chief clerk of the State Department, and was the only one of his siblings to outlive his father. Fletcher died at the 1862 Second Battle of Bull Run while serving as a colonel in the Union (American Civil War), Union army. Webster's younger son, Edward, died of typhoid fever in January 1848 while serving in the Mexican-American War. Webster's daughter, Julia, married Samuel Appleton Appleton, but died of tuberculosis in April 1848.
Conflicting opinions have been voiced as to his religion. The Unitarianism, Unitarian Universalist Church, citing ''Unitarianism in America'' from 1902, claim him as their own. Another source, the 1856 biography ''The American Statesman: The Life and Character of Daniel Webster'', proclaims him an avowed orthodox Trinitarian, baptized and raised in an Orthodox Congregational Church, and who died a member of the Episcopal Church. Remini writes that, though Webster occasionally attended other churches, he remained closely affiliated with the Congregational church throughout his life. In an 1807 letter to a Congregational pastor, Webster wrote, "I believe in the utter inability of any human being to work out his own Salvation, without the constant aids of the spirit of all grace. ... Although I have great respect for some other forms of worship, I believe the Congregational mode, on the whole, to be preferable to any other."
 Webster's legacy has been commemorated by numerous means, including the Daniel Webster Highway and Mount Webster in New Hampshire. His statue stands in the National Statuary Hall Collection, while another Statue of Daniel Webster (New York City), statue stands in Central Park. The ''USS Daniel Webster (SSBN-626)'' and the ''SS Daniel Webster'' were both named for Webster. The first Webster postage stamp was issued in 1870. In all, Daniel Webster is honored on 14 different US postage issues, more than most U.S. Presidents.Scotts US Stamp Catalogue There are 27 towns named for Webster in California, Webster,_Florida, Florida, Webster,_Illinois, Illinois, Webster,_Indiana, Indiana, Webster,_Iowa, Iowa, Webster,_Kansas, Kansas, Webster,_Kentucky, Kentucky, Webster,_Maine, Maine, Webster,_Massachusetts, Massachusetts, Webster,_Michigan, Michigan, Webster,_Minnesota, Minnesota, Webster,_Nebraska, Nebraska, Webster,_New Hampshire, New Hampshire, Webster,_New York, New York, Webster,_North Carolina, North Carolina, Webster,_North Dakota, North Dakota, Webster,_Ohio, Ohio, Webster,_Pennsylvania, Pennsylvania, Webster,_South Dakota, South Dakota, Webster,_Texas, Texas, Webster,_Virginia, Virginia, and Webster,_West Virginia, West Virginia, including two in Wisconsin (Webster, Burnett County, Wisconsin, Webster, Burnett County and Webster, Vernon County, Wisconsin, Webster, Vernon County), a ghost town in Colorado, and Webster and Webster Hollow in Tennessee. Seven County (United States), counties or List of parishes in Louisiana, parishes are named for Webster.
Webster's legacy has been commemorated by numerous means, including the Daniel Webster Highway and Mount Webster in New Hampshire. His statue stands in the National Statuary Hall Collection, while another Statue of Daniel Webster (New York City), statue stands in Central Park. The ''USS Daniel Webster (SSBN-626)'' and the ''SS Daniel Webster'' were both named for Webster. The first Webster postage stamp was issued in 1870. In all, Daniel Webster is honored on 14 different US postage issues, more than most U.S. Presidents.Scotts US Stamp Catalogue There are 27 towns named for Webster in California, Webster,_Florida, Florida, Webster,_Illinois, Illinois, Webster,_Indiana, Indiana, Webster,_Iowa, Iowa, Webster,_Kansas, Kansas, Webster,_Kentucky, Kentucky, Webster,_Maine, Maine, Webster,_Massachusetts, Massachusetts, Webster,_Michigan, Michigan, Webster,_Minnesota, Minnesota, Webster,_Nebraska, Nebraska, Webster,_New Hampshire, New Hampshire, Webster,_New York, New York, Webster,_North Carolina, North Carolina, Webster,_North Dakota, North Dakota, Webster,_Ohio, Ohio, Webster,_Pennsylvania, Pennsylvania, Webster,_South Dakota, South Dakota, Webster,_Texas, Texas, Webster,_Virginia, Virginia, and Webster,_West Virginia, West Virginia, including two in Wisconsin (Webster, Burnett County, Wisconsin, Webster, Burnett County and Webster, Vernon County, Wisconsin, Webster, Vernon County), a ghost town in Colorado, and Webster and Webster Hollow in Tennessee. Seven County (United States), counties or List of parishes in Louisiana, parishes are named for Webster.